The UAE has always been a world hub for trade and investment in part because of its friendly tax climate for business. There has never been a blanket-based corporate income tax in the country for decades. But with the passage of Corporate Tax in UAE, all of that changed. This may be a huge adjustment, but it is designed to set the UAE up to international standards without making the country less competitive to investors.
In this guide, we’ll break down what corporate tax really means, the applicable rates, who needs to register, and how companies can prepare for compliance and smarter planning.
What is Corporate Tax in UAE?
So, what is corporate tax exactly? Put simply, corporate tax is a tax on the earnings of a company. Unlike VAT, which is levied on consumption, corporate tax is levied on business revenues. That is, it is a direct tax on net earnings. It is because of this that most definitions call it corporate income tax.
For context, if we examine what corporate tax meaning in an international perspective, countries like the United States have long levied it, typically with much higher levels of rates than those in the UAE. Another point of distinction to note is between corporate tax vs income tax: income tax has a tendency to refer to individuals, while corporate tax refers to organizations. And yes, it is a direct tax as it is paid by the company directly and not passed on to customers.
Across the Middle East, governments have increasingly introduced forms of corporate income tax in an effort to diversify revenues. While the UAE is one of the newest to have done this, it remains one of the most business-friendly locations on Earth.
UAE Corporate Tax Rate
One of the most attractive features of the new regime is the UAE corporate tax rate. Designed to support small and medium enterprises and large companies alike, it strikes a middle ground between competitiveness and being aligned with global models.
This is how it is works:
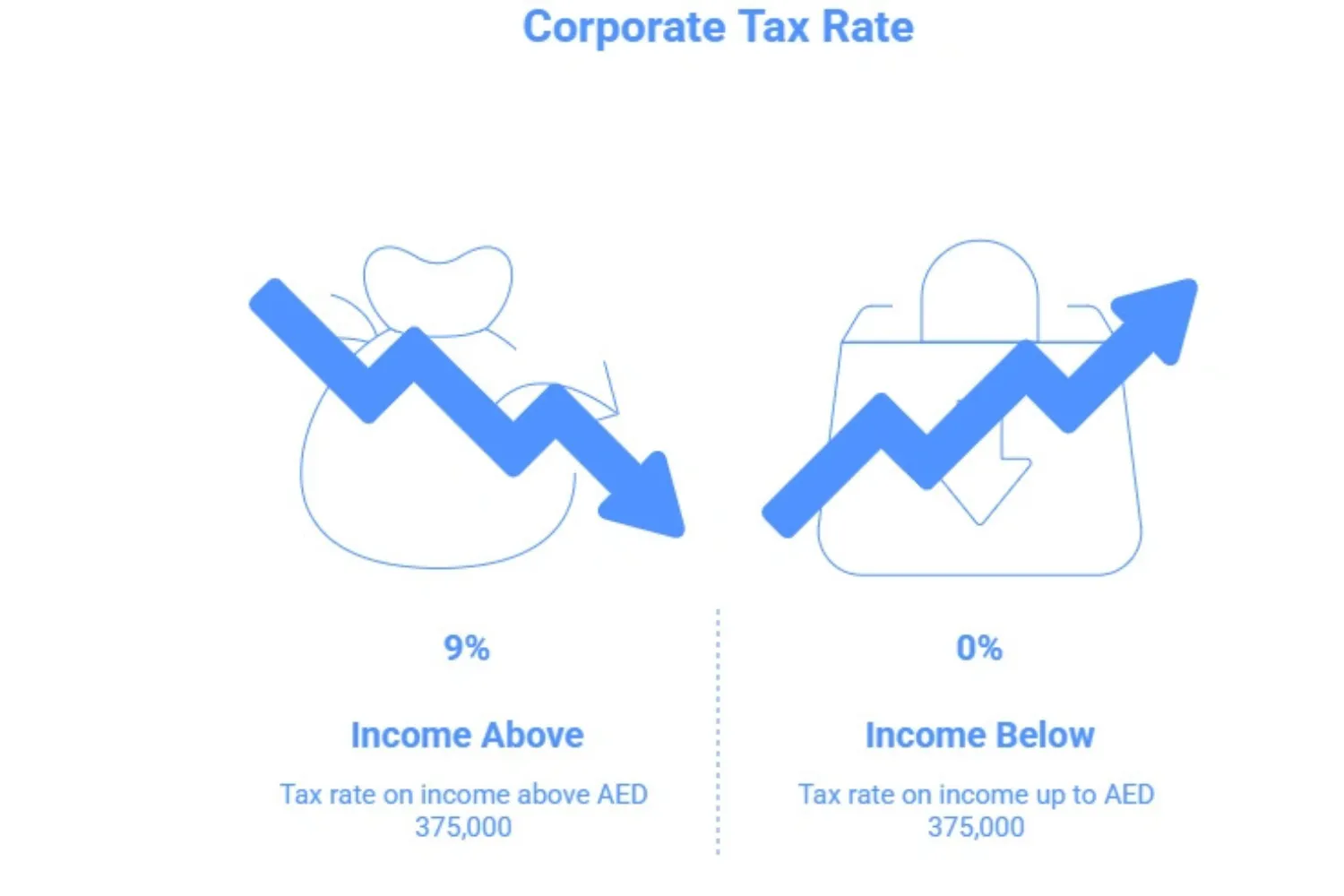
Regardless of whether you are operating in Abu Dhabi corporate tax rate, Dubai corporate tax rate, or any other Emirates, the rate is equally imposed across the UAE.
This structure is significantly lower than in most countries. For instance, the effective corporate tax rate on India is much higher, and double-digit rates are common in most developed economies. The UAE, however, positions itself as one of the low corporate tax countries, and consequently, it continues to be a persistent magnet for entrepreneurs.
In the future, the corporate tax reform UAE 2025 also discusses free zones regulations, multinationals, and reporting, ensuring that the system is compliant with international standards while being competitive.
Enquire Now
Who Must Register Corporate Tax?
Not every business in the UAE will be included under the new regime. So, who will be subject to register UAE Corporate Tax?
Juridical Persons: All companies established in the UAE, whether mainland or free zone companies established in the UAE are within its scope. That is, UAE Corporate Tax applies most registered businesses.
Government Entities: Certain government-owned entities are exempted, but commercial activities of government entities may be required to register.
Individuals: Salaries are out of scope but if one holds a commercial license and earns business income, then corporate income tax UAE regulations apply.
Non-Residents: Businesses that have a permanent establishment in the UAE must be registered.
There also exist reliefs like Small Business Relief, which reduce the compliance cost for small businesses. However, CT will not apply to on entities in extractive industries already subject to Emirate level taxes, or on certain government entities.
Briefly stated, if you operate a business within the nation, corporate tax registration UAE will most likely be required.
Also Read: Corporate Tax Registration for Free Zone Companies in the UAE
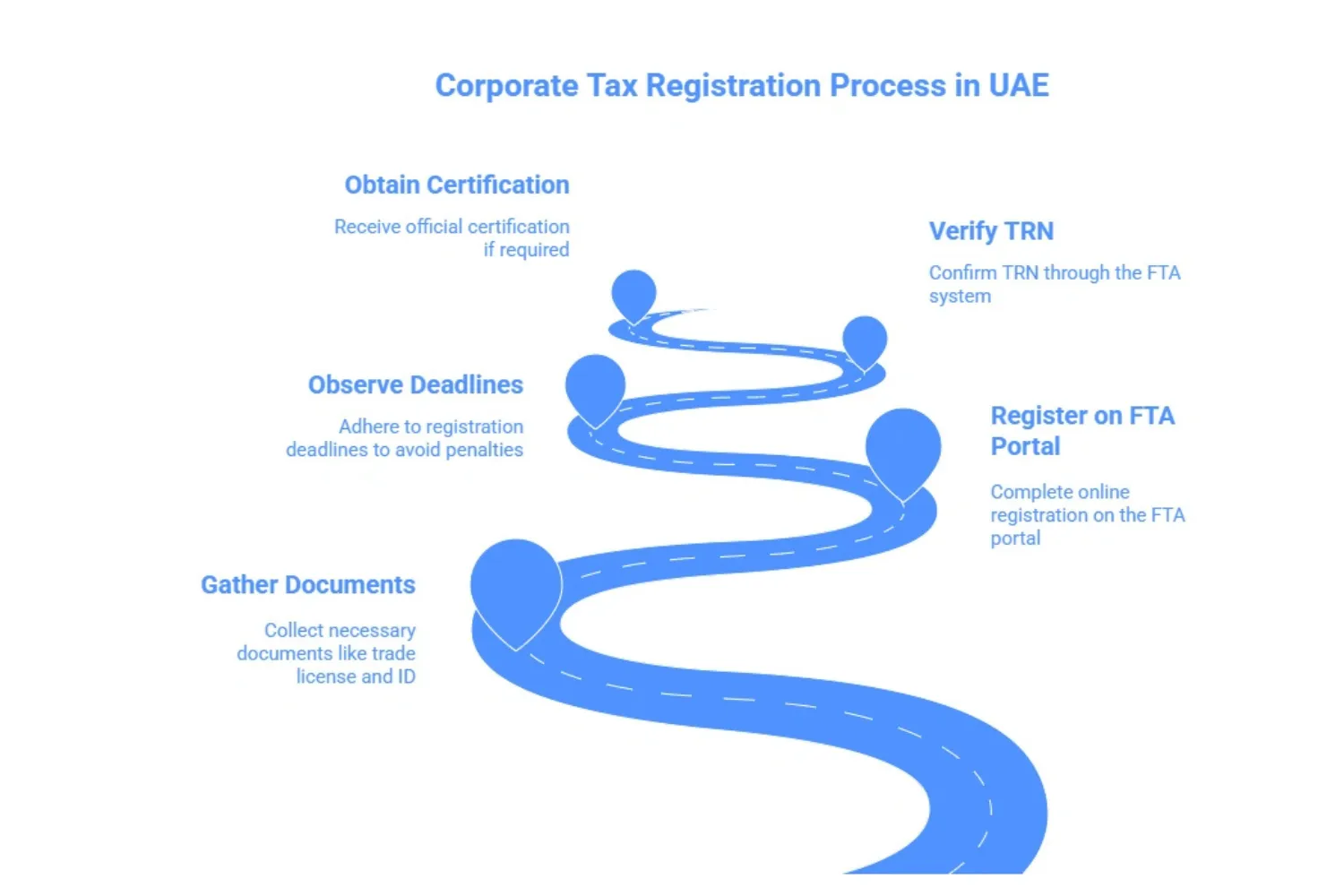
Step-by-Step Guide To Corporate Tax Registration in UAE
So how do you actually register? The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) does the registration.
Get your documents: These are your trade license, incorporation documents, passport/Emirates ID of owners, and financial year information.
FTA portal: Businesses should register online on the FTA portal in order to obtain a UAE tax registration number (TRN).
Deadlines: Observe the corporate tax registration deadline UAE and the last date notified by authorities, late submission attracts penalties.
Verification: The FTA system may request TRN verification by company name to confirm records.
Certification: Organizations may at times be needed to provide a certificate of incorporation UAE or such documents.
Whether you call it tax registration Dubai or FTA registration UAE or even corporate tax registration, it is all unified under the FTA. To be current is of utmost importance.
Corporate Tax Compliance & Filing
Registration is only the first start ongoing compliance is just as important. Companies need to know when and how to file corporate tax return requirements.
Key Takeaways :
| Topic | Key Information |
| Filing Deadline | Returns must be filed within 9 months from the end of the financial year. |
| How to Submit | Online submission through the FTA portal; corporate tax software solutions available for ease. |
| Payment | Corporate tax can be paid online directly via the FTA website. |
| Penalties | Late filing or delayed payment leads to fines and interest. |
| Installments | Tax installment options may be available in certain cases to ease cash flow. |
| Support | Companies often use corporate tax accountants, outsourcing, or return services for efficiency and accuracy. |
Compliance can be seen as paperwork, but staying on track avoids massive costs and gives seamless operations.
Corporate Tax Planning & Advisory
Filing is just half the battle. Smart business also takes notice of corporate tax planning. Done well, it minimizes cost at the same time that it maintains compliance.
This is what effective corporate tax planning strategies:
- Identifying of corporate tax incentives and corporate tax exemptions.
- Application of corporate governance incentives in a prudent manner without taking recourse to aggressive tax avoidance strategies.
- Consulting corporate tax advisory services, such as experienced corporate tax consultants or corporate tax lawyers, to guide on structuring, deductions, and compliance.
- Dependence on corporate tax preparation services to double-check everything to make it accurate before submission.
Tax planning turns tax into a manageable part of business management instead of a weight.
Corporate Tax for Individual Entities
Not all companies are alike. This is how Corporate Tax in UAE works differently for different entities:
Free Zone Corporate Tax: Companies in free zones may benefit from 0% tax if they qualify as “Qualifying Free Zone Persons.” Non-qualifying entities face the standard 9% rate.
Multinational Companies in UAE: Large MNCs, whether in Dubai or Abu Dhabi, must also consider international rules such as the OECD’s Pillar Two.
SMEs and Startups Corporate Tax: Smaller firms benefit from the AED 375,000 threshold, which eases the early-stage burden.
Oil and Gas / Natural Resources: Sectors like corporate tax oil and gas Dubai or corporate tax oil trading UAE may face specific regimes at the Emirate level, separate from general corporate tax.
Each type of entity must review its situation closely in order not to misinterpret.
Conclusion
The Corporate Tax in UAE is a landmark reform, but one that can be navigated with relative ease. With aggressive rates, exemptions, and open filing rules, the UAE still manages to reconcile global compliance with its pro-business culture.
By registering on time, keeping accurate records, and leveraging advisory support, companies can transform corporate tax from a risk into a manageable routine. Whether you’re a startup, a free zone entity, or a multinational, understanding the framework ensures you’re always ahead of deadlines, compliant, and prepared for growth.
FAQs For Corporate Tax
Corporate tax is paid by companies and other legal entities that earn taxable profits within the UAE, subject to exemptions defined by law.
In the UK, corporate tax called corporation tax is paid by limited companies on their taxable profits, similar to the UAE but with different rates and rules.
Yes, in certain cases the UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA) allows installment plans to ease cash flow, but businesses must apply and meet eligibility criteria.
UAE corporate tax is calculated by applying the 9% tax rate on taxable income above AED 375,000 after adjusting for deductions, exemptions, and non-deductible expenses.
Corporate income tax rebates are reductions or refunds offered under specific conditions, helping businesses lower their effective tax liability.
A corporate tax return in the UAE is due nine months after the end of the company’s financial year.
Payment is made along with the tax return filing, also within nine months of the end of the financial year.
The UAE corporate tax registration deadline is set by the FTA and varies depending on the entity’s license issuance month.
The UAE corporate tax rate is 9% on taxable income exceeding AED 375,000, with 0% applied below that threshold.
All UAE companies, free zone entities, and foreign businesses with taxable income in the UAE are subject to corporate tax unless exempt.
It applies to onshore companies, free zone entities (subject to qualifying conditions), and foreign businesses generating UAE-sourced income.
Any company or legal entity carrying out business in the UAE that is not specifically exempt must register for corporate tax.
Businesses register online through the FTA’s Emaratax portal by submitting required documents and details of their trade license.
Corporate tax registration in the UAE is done via the Emaratax portal and is mandatory for all eligible businesses.
The process involves creating an Emaratax account, filling in registration details, uploading documents, and receiving a Tax Registration Number (TRN).
Log into the FTA’s Emaratax system, complete the application, attach documents like trade license and financials, and submit.
Dubai tax registration is part of UAE corporate tax registration and is completed through the Emaratax portal.
Businesses in Dubai must register through Emaratax to comply with corporate tax law.
This refers to the mandatory process of enrolling a business with the FTA to obtain a TRN for corporate tax.
Businesses can log in to Emaratax (tax.gov.ae) using their UAE Pass or registered credentials to manage tax registration and filings.
You can update your trade license details by logging into Emaratax, going to the “Taxpayer Profile” section, and uploading the updated license.
Corporate Tax in the UAE is a federal tax on the profits of companies, set at 9% above AED 375,000, introduced in June 2023.
All businesses operating in the UAE, unless exempt, must register for corporate tax through the FTA.
Corporation tax cannot be avoided, but businesses can minimize liability legally through deductions, exemptions, and strategic tax planning.
0% on income up to AED 375,000, and 9% on taxable income above that threshold.
Exemptions apply to government entities, certain natural resource businesses, and qualifying public benefit organizations.
Typically, businesses need their trade license, owner details, financial statements, and Emirates ID copies of shareholders/partners.
Step 1: Create an Emaratax account. Step 2: Submit business details. Step 3: Upload documents. Step 4: Receive TRN confirmation.
Tax returns are filed electronically on Emaratax within nine months of the financial year end.
Businesses register through the FTA’s Emaratax portal using UAE Pass or login credentials.
Registration is completed only on the official FTA platform, Emaratax.
Log into Emaratax, fill in tax registration form, upload trade license and documents, submit and await TRN.
